Stop chasing the prompt engineering hype. The true AI skills for 2026 are strategic, systemic, and command the highest salaries in the market. This authoritative, comprehensive guide, based on research from thousands of industry professionals, reveals the four core functional areas: Generalists, Product, Engineering, and Marketing, that are being redefined by automation.
We dive deep into the specific, high-value skills that will determine success in the coming years, from mastering Agentic Workflows for enterprise systems and designing Context Engineering pipelines, to leveraging RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) for accuracy and pioneering Answer Engine Optimization (AEO). The Future of work automation demands professionals who can build systems that move a 10-hour task to 1 minute. Learn the exact roadmap to transition from being a consumer of AI to an architect of the next generation of business efficiency.
If you are still banking on “prompt engineering” as your ticket to a six-figure salary, I have some difficult news: that ship has sailed. The digital landscape is shifting rapidly, and the AI skills for 2026 are no longer about asking a chatbot a clever question; they are about building systems, designing architectures, and fundamentally reshaping how businesses operate.
We recently analyzed data from over 4,500 professionals with a median of 10 years of experience and reviewed thousands of job descriptions to answer one critical question: What actually moves the needle?
The answer isn’t better prompts. It is the ability to integrate Artificial Intelligence into the core functions of an organization. In this guide, we are looking at the future of work automation and the specific, high-value skills required for Generalists, Product Managers, Engineers, and Marketers to thrive.
The New Mandate for Generalists: From 10 Hours to 1 Minute
Whether you are a Chief of Staff, a COO, an Operations Head, or a Strategy Lead, your title doesn’t matter as much as your mandate. In the coming years, the defining metric of your success will be efficiency. Your core job description is shifting to a singular challenge: If a task currently takes 10 hours, can you build a system that does it in 1 minute using AI?
To survive the shift toward the future of work automation, generalists must master three specific competencies.

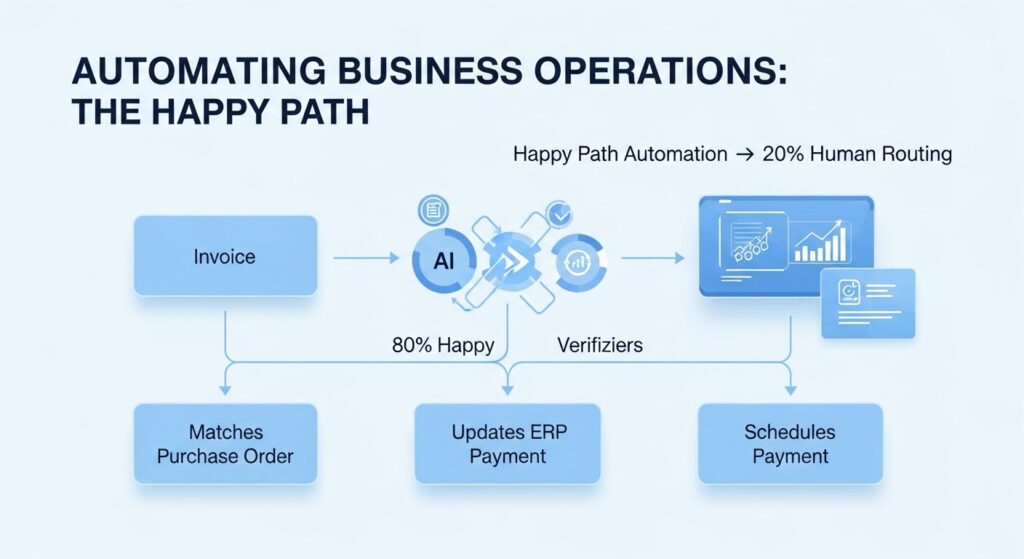
1. Automating Business Operations (The “Happy Path”)
Business operations are essentially repeated processes: employee onboarding, customer support ticketing, or invoice processing. Traditionally, these operations are linear and human-heavy.
Consider the standard invoice lifecycle:
- An invoice arrives.
- A human extracts the data.
- Someone matches it to a purchase order.
- Another person approves it.
- Finance processes the payment.
In this scenario, five humans touch one document. This is where AI skills for 2026 come into play. A skilled generalist builds an automation layer where the AI extracts data, matches the PO, verifies amounts, updates the ERP, and schedules payment, with zero human intervention required for the standard case.
Note on The “Happy Path”: Automation thrives on the “Happy Path” the 80% of scenarios where everything goes as planned. If an invoice has a handwritten note saying “Approved by CFO in Tuesday’s meeting,” a rigid workflow will fail. Your job is to automate the 80% predictable work and route the complex 20% to humans.
Major players are already doing this. For instance, Flipkart reduced its vendor onboarding time from 4 days to just 4 hours using these exact principles.
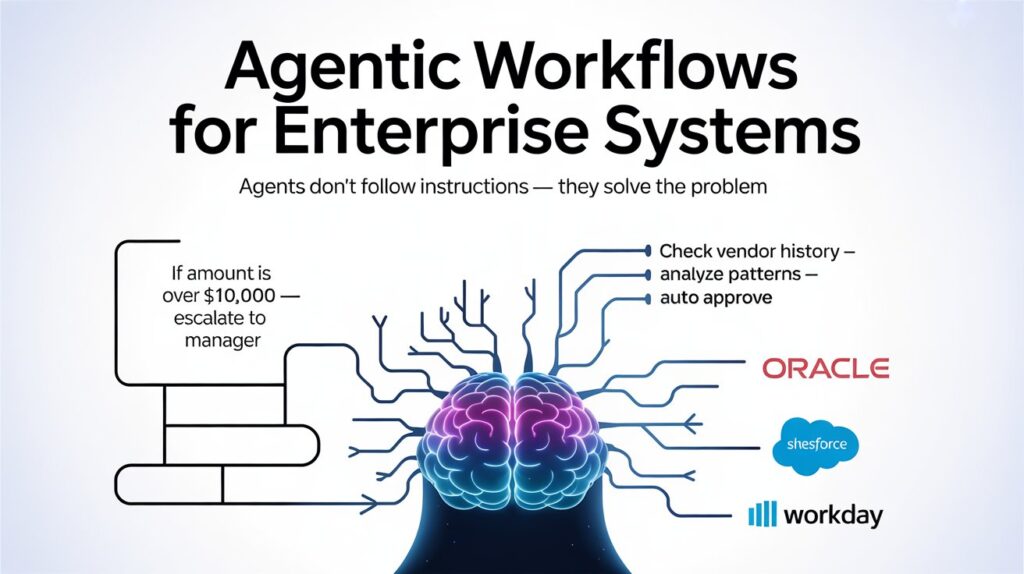
2. Agentic Workflows for Enterprise Systems
This is perhaps the most critical distinction for 2026. You must understand the difference between a Workflow and an Agent.
- Workflows follow a set of strict rules (If X, then Y).
- Agents have a goal and can create their own rules to achieve it.
Let’s look at an example in the context of invoice processing. A standard workflow might see a $10,000 invoice, and based on a hard rule, escalate it to a manager every single time. However, an AI Agent analyzes the context. It recognizes the vendor is a regular supplier, checks monthly ordering patterns, reviews previous CFO approvals, and might decide to approve it instantly because it falls within safe historical parameters.
The agent doesn’t just follow instructions; it solves the problem.
According to Y Combinator, one of the world’s most prestigious startup accelerators, there is a massive demand for people who can build these agentic flows. Fortune 500 companies run on tens of thousands of software systems, such as Salesforce, Oracle, Workday, and 73% of their business processes still require human intervention. Building agents that bridge these gaps is predicted to be one of the highest-paying AI skills for 2026.
3. AI Adoption Strategy
You can build the most sophisticated agentic workflows in the world, but they are useless if your 10,000 employees refuse to use them. This is where most digital transformations die. Consequently, one of the most critical AI skills for 2026 is actually a hard strategy: managing human fear.
Sales teams fear AI will replace relationships, while Finance and Legal worry about compliance and liability. Developing a robust adoption framework is a core component of essential AI skills for 2026 because it creates trust. Employees need to know what the AI is doing, where it might go wrong, and that they remain in charge. LinkedIn data validates the explosion of these AI skills for 2026, noting that “AI Strategy” profiles grew from 5,000 in 2022 to over 50,000 in 2024.
The future of work automation isn’t just about code; it’s about culture. If you can bridge the gap between technical capability and human adoption, you become indispensable.
The Evolution of Product Management
Moving beyond operations, the product function is undergoing a radical overhaul. For Product Managers (PMs), simply “sprinkling AI” on existing features is a recipe for failure.
AI Product Strategy: The Triage Method
Think of AI Product Strategy like a hospital triage unit. Not every patient needs surgery; some just need a bandage. Similarly, not every feature needs a Large Language Model (LLM).
Bad PMs say, “Let’s put AI in our search bar because it looks cool.” Good PMs ask, “Where will AI actually move the needle on revenue, retention, or conversion?”
Real-World Example: Imagine a SaaS company with 8% churn.
- The Bad Strategy: Build a generic AI support chatbot to save $20,000 a year.
- The Winning Strategy: Data shows users churn because they don’t activate within 7 days. You build an AI Onboarding Assistant that guides new users, cutting churn by 3%. That is worth $2 million annually.
Developing the judgment to know where to apply these AI skills for 2026 and distinguishing between hype and business value is what separates junior PMs from product leaders.

AI Prototyping: From Specs to Software in an Hour
The second critical skill for Product Managers in the era of AI skills for 2026 is AI Prototyping. The traditional product development cycle is slow and expensive: you have an idea, you write a specification document, engineers spend weeks coding it, and only then do you discover if the idea actually works. If it doesn’t, you have burned a month of development time, a failure that advanced AI skills for 2026 can prevent.
AI prototyping completely disrupts this workflow. To truly leverage AI skills for 2026, the standard will not be wireframes or mockups; it will be functional software. Using AI coding assistants and low-code platforms, you can now build a working version of your idea in an hour, one that users can actually click, interact with, and test.
Vishal Virani, founder of Rocket, demonstrated this shift by helping companies go from a raw idea to a working product in minutes. This isn’t about replacing engineers; it is about validating the future of work automation rapidly. Ultimately, applying AI skills for 2026 ensures that when engineers do write code, they are building something proven to work.

The Convergence: Critical Skills for Product & Engineering
As we move deeper into the technical stack, the line between Product Management and Engineering begins to blur. The following AI skills for 2026 are mandatory for both roles, though they approach them from different angles.
1. Context Engineering (The “New” Prompt Engineering)
If you take one thing away from this guide, let it be this: Context Engineering > Prompt Engineering.
Most people think the secret lies in telling the AI to “act as a senior developer.” That is beginner-level thinking. Context engineering is about designing the entire system that surrounds the AI so it can figure things out for itself without perfect prompts.
Consider this example: You tell an AI agent, “Book me a hotel in Paris for the DevOps conference next month.”
- The Failure: The AI books a Best Western in Paris, Kentucky.
- The Diagnosis: Was this a prompt problem? No. It was a context problem.
In a properly engineered system, the agent should automatically check your calendar to see exactly where the conference is located (Paris, France). It should retrieve your company’s travel policy to understand budget limits. It should access past conversations to know your hotel preferences.
- The PM’s Role: Designing the context flow. What information does the AI need at each step to succeed?
- The Engineer’s Role: Building the retrieval pipeline, managing token limits, and handling failures.
Mastering context engineering is essential for the future of work automation because it removes the cognitive load from the human user.

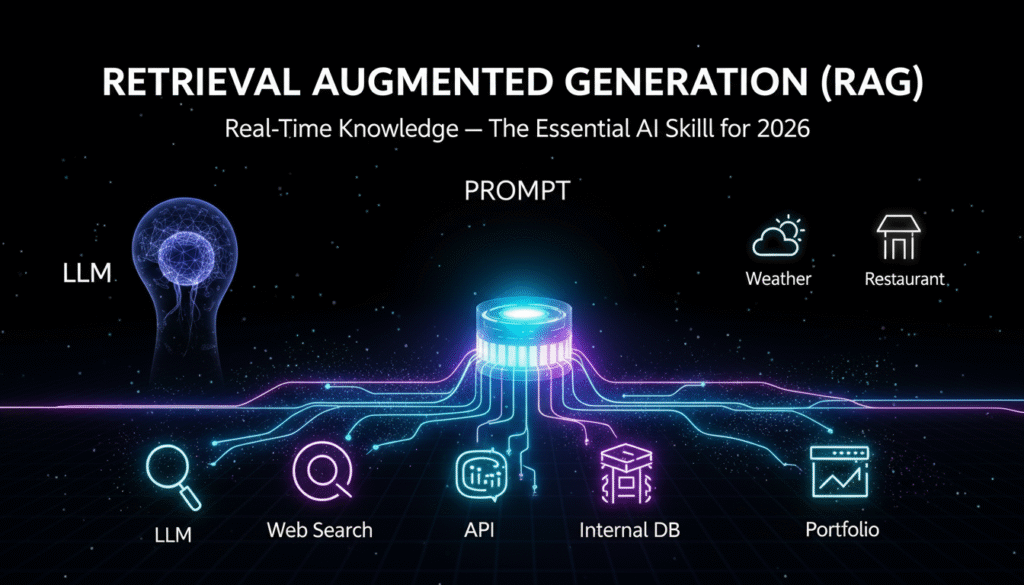
2. RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
To understand RAG, try to guess the exact temperature outside right now without looking at your phone. You might guess “30°C” or “it’s pleasant.” You know the general feeling, but you don’t store the precise data point in your brain. Recognizing this gap is the first step in mastering AI skills for 2026.
AI models work the same way. If you ask a standard model, “What is the current temperature in Bangalore?”, it has no clue. It knows climate patterns that December is pleasant, but it is essentially hallucinating a probability.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is the architecture that allows the AI to “look at its phone.” Implementing RAG is one of the definitive AI skills for 2026 because it enables the system to search the web or your internal database to fetch exact, real-time data.
For companies like Swiggy or Zerodha, these AI skills for 2026 are non-negotiable. A Swiggy AI chatbot cannot guess if a restaurant is open; it needs real-time operational status. A Zerodha AI cannot estimate your portfolio value; it needs to pull your actual holdings.
In 2026, building “smart” chatbots without RAG will be unacceptable. The ability to architect systems that combine the reasoning power of LLMs with the accuracy of real-time data is one of the most technical AI skills for 2026.
3. Building True AI Agents
There is a massive misconception in the market: people confuse “Models” with “Agents.”
- The Model (e.g., GPT-4): This is just the brain. It generates text. It doesn’t do anything.
- The Agent: This is the system that decides what to do with that brain.
When you use ChatGPT, you aren’t just talking to a model; you are interacting with an agent that decides, “Should I run Python code? Should I search the web? Should I generate an image?”
Microsoft predicts that 87% of Fortune 500 companies will be deploying agents by the end of 2026. The lucrative jobs won’t be in building new Large Language Models (companies like OpenAI and Google have that covered). The money is in building the agents that utilize those models to perform business tasks.
- Engineering Focus: Tool integration, state management, and guardrails (preventing the agent from burning through your API budget).
- Product Focus: Defining the workflow, approval paths, and failure scenarios.
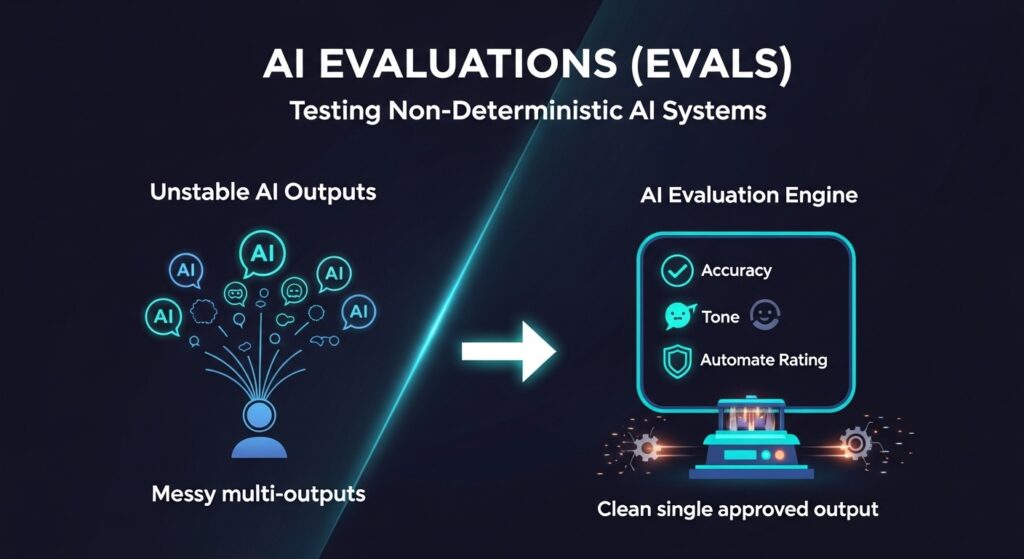
4. AI Evaluations (Evals)
You have built your AI feature. Now, how do you know if it works?
Traditional software testing is deterministic: if you input “2+2”, the code should always output “4”. If you run test 1,000 times, you get the same result. AI is different. You can ask an AI the same question twice and get two different answers. Both might be right, or both might be wrong.
This non-deterministic nature makes AI Evaluations a critical skill. Leading voices from OpenAI, Amazon, and Y Combinator agree that “AI Evals” is the missing link in the future of work automation. You need to build automated frameworks that can grade AI responses on accuracy, tone, and safety at scale. Without this, you cannot deploy AI products with confidence.
Marketing: The Shift to Answer Engines
Marketing is perhaps the function most visibly disrupted by AI. As search behavior changes, the skills required to capture attention are shifting from traditional SEO to something entirely new.
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)
For the last two decades, the goal was to rank on Google. But today, users are asking AI for answers directly. If a user asks ChatGPT, “What are the top Asian restaurants near me?” does your brand show up in that generated response?
This is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO). With over 2 billion searches already happening inside AI agents and data suggesting that users coming from AI chat interfaces have a 2x higher intent to buy than those from traditional search, AEO is set to become the hottest marketing skill.
The AI skills for 2026 for marketers involve understanding how LLMs aggregate information and ensuring your brand’s digital footprint is structured in a way that AI “trusts” and cites it. It is no longer just about keywords; it is about brand authority within the AI’s training data and retrieval sources.
AI Ad Generation: The End of the “Big Idea” Bottleneck
If AEO is about being found, AI Ad Generation is about being seen.
Traditionally, creating a high-quality video ad was a logistical nightmare: months of planning, expensive shoots, actors, and endless post-production loops. In 2026, this model is obsolete.
Major brands are now generating broadcast-quality ads using AI in a fraction of the time. But the real “skill” here isn’t just making a video; it is Rapid Iteration.
- Old Way: Wait weeks for user insights — Brief designers — Wait for creative — than Launch one ad.
- New Way: Get an insight at 9:00 AM — Generate 5 ad variations by 10:00 AM — Launch and test by noon.
The future of work automation in marketing relies on this velocity. You aren’t just a creative director; you are a high-frequency trader of attention.
AI-Led Performance Marketing: The One-Person Agency
As ad generation scales, managing campaigns becomes impossible for humans alone. This brings us to AI-Led Performance Marketing.
In 2026, the grunt work of performance marketing, adjusting bids, reallocating budgets, and shifting targeting parameters will be fully autonomous. The skill you must master is Orchestration.
An AI agent can sift through thousands of data points in real-time to rotate creatives and optimize spend based on live performance data.
- The Impact: A single marketer equipped with these AI skills for 2026 can do the work of a 4-person agency team.
- The Value: If you are spending approx $120k a month on ads, even a 3% AI-driven optimization saves you vast sums annually. Your job is to set the strategy and guardrails, letting the AI handle the execution.
AI Content Production: Scale Without Compromise
Finally, we have AI Content Production. We have all seen the AI clones (like the Varun Mayya examples) taking over social media. But the competitive advantage isn’t “using AI”; it is Production at Scale.
Instead of manually filming five high-quality videos, AI allows creators to produce 50 videos for the same cost. This saturation strategy is critical for staying relevant in a noisy digital world.
Bonus: AI Skills Across Every Function
While we have focused on Generalists, PMs, Engineers, and Marketers, the future of work automation touches every role. Here is a quick breakdown of how other functions are evolving:
- HR & Talent: The focus is shifting to AI-powered Talent Matching. It’s no longer about reading resumes; it’s about using AI agents to match candidate profiles with deep organizational needs and predicting retention before an offer is even made.
- Sales: The cold email is dead. The new skill is Hyper-Personalized Outreach at Scale. Sales professionals are using AI to research a lead’s recent news, company reports, and LinkedIn activity to generate highly specific messages that actually get responses.
- Analytics: Analysts are moving from “reporting data” to building Recommendation Engines. The AI doesn’t just tell you what happened; it tells you what to do next.
Summary: Your Roadmap to 2026
We are less than two months away from 2026. The window to build your unfair advantage is closing, but it is not shut yet. Here is your recap of the essential AI skills for 2026:
| Role | Core AI Skills to Master |
| Generalist | Automating Operations, Agentic Workflows, AI Adoption Strategy |
| Product Manager | AI Product Strategy, AI Prototyping, Context Engineering |
| Engineer | RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation), Building Agents, AI Evals |
| Marketer | AEO (Answer Engine Optimization), AI Ad Gen, Performance Marketing |
Final Advice:
Do not try to learn everything. The people who mastered digital marketing in 2010 weren’t smarter than you; they just started earlier. Pick one skill from this list that aligns with your function. Start today. By the time 2026 arrives, you won’t just be participating in the AI revolution you will be leading it.
(FAQs):
Q1: Will AI replace my job by 2026?
A: AI is unlikely to replace your job entirely, but it will replace the tasks you do today. Professionals who master AI skills for 2026, specifically those who can manage agents and workflows, will replace those who refuse to adapt.
Q2: What is the difference between Prompt Engineering and Context Engineering?
A: Prompt engineering is about writing a good question for a chatbot. Context engineering is about designing the system around the AI, giving it access to calendars, budgets, and past data so it can solve problems autonomously without needing a perfect prompt.
Q3: I am non-technical. Can I still build AI Agents?
A: Yes. The rise of low-code and no-code AI platforms means Generalists and PMs can now build functional agents. The primary skill required is logic and workflow design, not raw Python coding.
Q4: Why is “AI Adoption Strategy” considered a hard skill?
A: Because the best technology fails if humans don’t use it. Managing the fear, compliance issues, and cultural resistance to the future of work automation is a measurable, high-value strategic skill.
Q5: What is RAG and why is it important?
A: RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) allows AI to “look up” facts from real-time data (like current stock prices or inventory levels) rather than guessing. It is essential for building trustworthy business applications.




